- Published on
Securely connect GitLab Self-managed to CircleCI using IP ranges feature
- Authors

- Name
- Tadashi Nemoto
- @tadashi-nemoto

This article describes how to securely connect GitLab Self-managed to CircleCI using the IP ranges feature.
- CircleCI now supports GitLab Self-managed
- CircleCI's IP ranges feature
- Prerequisites
- Allow CircleCI IP addresses in GitLab Self-managed
- Set up a project
- Create pipelines that enable IP ranges
- Build and push docker images using Kaniko
- If you want to use macOS for iOS CI/CD pipelines
- Notes
CircleCI now supports GitLab Self-managed
CircleCI upgrades to GitLab integration with support for GitLab self-managed.
Announcing GitLab support on CircleCI | CircleCI
You can host and run GitLab CI on your GitLab Self-managed server instance, but you will face the following difficulties:
Slower build speeds and limited job parallelism
Difficulty using macOS for iOS CI/CD pipelines
Lack of core CI/CD features required by developers, such as debugging, visualization, security features, and test partitioning
Fortunately, developers who use GitLab self-managed can now use CircleCI's best-in-class CI/CD solution.
However, there is one challenge when connecting GitLab Self-managed to CircleCI. The GitLab self-managed instance must be accessible via the public internet.
This is rightly seen by engineers as a security risk.
Luckily, this risk can be mitigated by using CircleCI’s IP ranges feature to securely connect GitLab Self-managed to CircleCI using IP allowlisting.
CircleCI's IP ranges feature
SaaS CI/CD tools usually do not have a fixed IP address range and can be difficult to connect to environments with firewalls.
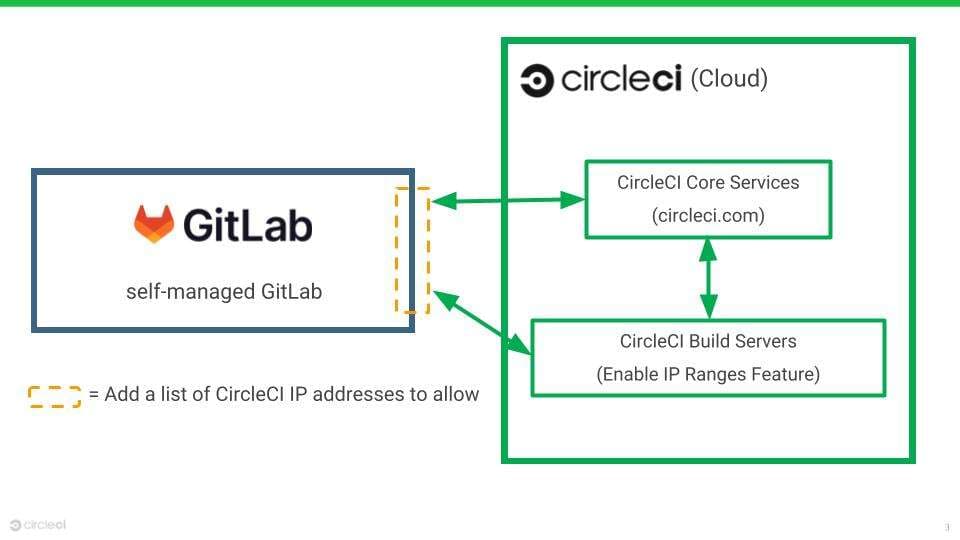
When the IP ranges feature is enabled on a Docker job through a config file, CircleCI re-routes any outgoing communication through one of about 30 IP addresses listed in the documentation.
This allows you to restrict inbound traffic to your GitLab instance to only CircleCI’s IP address.
IP ranges - better security for more confidence | CircleCI
In this article, we will use this IP ranges feature to allow CircleCI to connect to GitLab Self-managed as shown in the diagram below.
Prerequisites
GitLab Self-managed
- Available in both Community Edition and Enterprise Edition
- This time, GitLab Self-managed is installed using Helm Chart
CircleCI
- The IP ranges feature is available to customers on a Performance or Scale plan.
Allow CircleCI IP addresses in GitLab Self-managed
First, configure GitLab Self-managed to allow the following IP addresses.
IP addresses for core services
- Used to trigger jobs, exchange information about users between CircleCI and GitLab etc
In this example, I’ve installed GitLab Self-managed via a Helm Chart. We can allowlist IP addresses using loadBalancerSourceRanges in the NGINX Ingress Controller Helm Chart.
nginx-ingress:
controller:
service:
loadBalancerSourceRanges: [
# IP Ranges
3.228.39.90/32
18.213.67.41/32,
34.194.94.201/32,
34.194.144.202/32,
34.197.6.234/32,
...
# Core
18.214.70.5/32,
52.20.166.242/32,
18.214.156.84/32,
54.236.156.101/32,
...
helm upgrade --install gitlab gitlab/gitlab --values gitlab_config.yaml
Set up a project
Next, set up your project with GitLab Self-managed connected to CircleCI with IP addresses allowed.
Follow the GITLAB SELF-MANAGED instructions in the following document to set it up.
GitLab integration overview - CircleCI
Create pipelines that enable IP ranges
Once the project is set up, create a pipeline with the IP ranges feature enabled.
Add the circleci_ip_ranges: true flag to enable the IP ranges feature for all jobs.
jobs:
unit_test:
circleci_ip_ranges: true # Enable IP ranges feature
docker:
- image: cimg/node:18.14.0
steps:
- checkout
- node/install-packages
- run: npm run test:ci
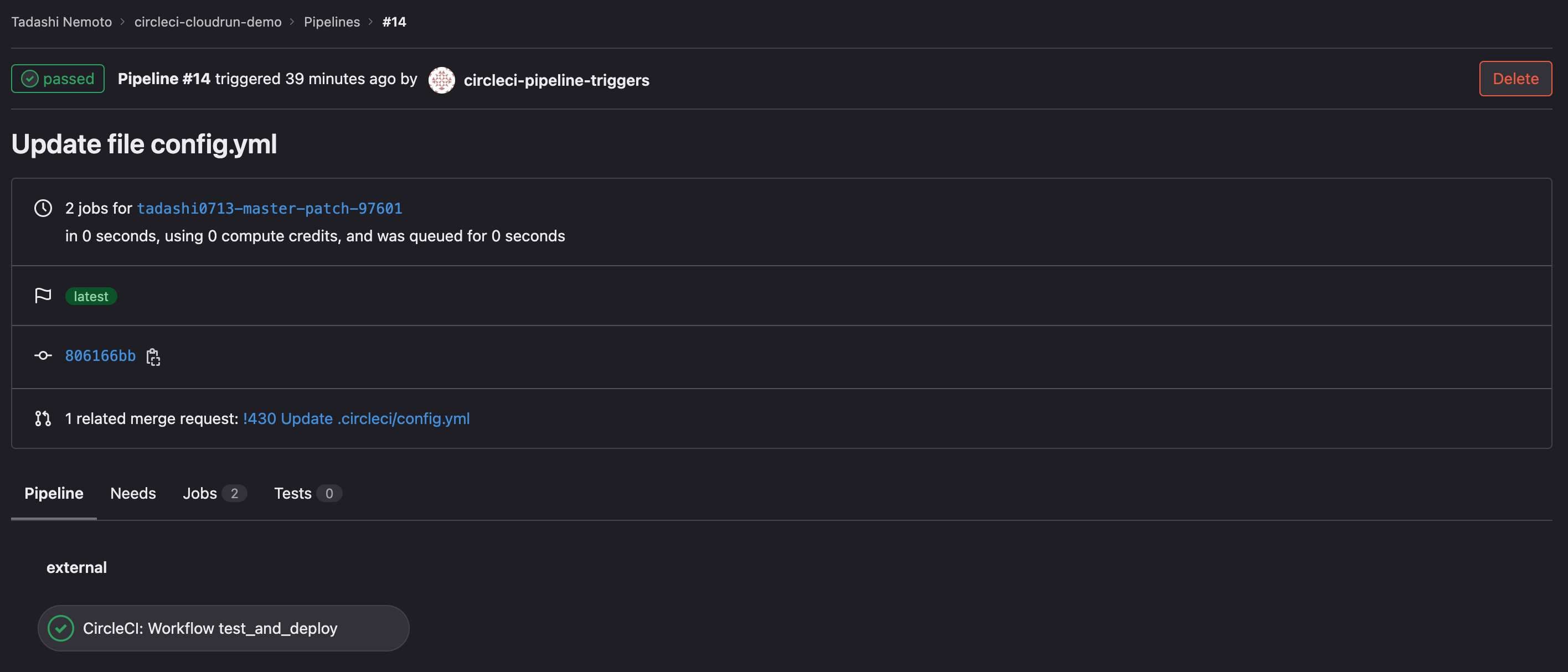
Once your pipeline configuration file(.circleci/config.yml) has been pushed to GitLab, GitLab sends a webhook to CircleCI to trigger a pipeline.
You can check the pipeline’s status from the CircleCI UI.
You can also check it in the GitLab UI under “Merge Requests”.
Build and push docker images using Kaniko
The IP ranges feature is currently available exclusively for the Docker Executor, not including remote_docker.
Therefore, it is usually not possible to build and push Docker images for the following reasons:
Machine Executor (e.g. Linux VM) cannot be used
DinD (Docker in Docker) within the Docker executor
However, DinD (Docker in Docker) can be avoided by using Kaniko even in Docker Executor.
This allows you to build and push Docker images to each repository (Docker Hub, Amazon ECR, Azure Container Registry) with the IP ranges feature enabled.
The following is an example of a job that uses Kaniko to build and push a Docker image to DockerHub with the IP ranges feature enabled:
kaniko-build-push-docker-hub:
circleci_ip_ranges: true # Enable IP ranges feature
environment:
DOCKER_REGISTRY: docker.io
docker:
- image: gcr.io/kaniko-project/executor:debug
entrypoint: ''
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: add Docker Hub credentials
command: |
mkdir -p /kaniko/.docker
./config.sh
mv config.json /kaniko/.docker
- run:
name: Build and Push image
command: |
/kaniko/executor \
--context "$(pwd)" \
--dockerfile "$(pwd)/Dockerfile" \
--destination "${DOCKER_REGISTRY}/tadashi0713/gitlab-kaniko:${CIRCLE_SHA1}"
For more information, please refer to the following document.
How-to: build and push Docker images with Kaniko - Tips, Tricks and Hacks - CircleCI Discuss
If you want to use macOS for iOS CI/CD pipelines
CircleCI offers cloud-native macOS VMs and IP address ranges of them are available.
You can connect to these macOS VMs by configuring GitLab Self-managed to allow the above IP address ranges, as shown below:
nginx-ingress:
controller:
service:
loadBalancerSourceRanges: [
# macOS
162.252.208.0/24,
162.252.209.0/24,
192.206.63.0/24,
162.221.90.0/24,
38.39.177.0/24,
...
- macOS builds are automatically restricted within the IP ranges listed here. In other words, you do not have to explicitly set
circleci_ip_ranges: truefor macOS builds.
CircleCI also offers M1 Macs, which can significantly improve the performance of iOS CI/CD pipelines.
Build on Apple silicon with M1 support for CI/CD pipelines
CircleCI M1 Mac performance comparison
Notes
The IP ranges feature is available to customers on a Performance or Scale plan.
The IP ranges feature is currently available exclusively for the Docker Executor, not including
remote_docker. Jobs that attempt to use the IP ranges feature with a Machine executor, or withsetup_remote_docker, will fail with an error.The IP ranges feature costs 450 credits per GB of data used by jobs with the feature enabled.